Data sharing, which will guide how systems and devices respond with greater automation and interconnectivity to help us optimize our lives at home and at work, is probably the most crucial element to realizing a world bright society. This will be done with the aid of sophisticated AI-driven analytics, modeling, and decision-making.

Driving Sustainability Through Data Sharing: Mitsubishi Electric’s Vision for a Circular Digital-Engineering in a Smart Society
Although this observation may be simple, it’s crucial to understand the scope and magnitude of the work involved in creating and putting into place the technologies and systems needed to benefit from this data sharing, let alone on a worldwide scale.
The business strategy of Mitsubishi Electric is centered on fostering a international, sustainable smart society. M.E. is in a special position to gather data-driven, cross-industry business insights that will enhance our offerings given our capabilities in fields like power, transportation, home appliances, infrastructure, manufacturing, IT/communications, and others. As a result, our customers will be able to accomplish their business objectives and, over time, solve major cultural issues like accelerating decarbonization, optimizing the use and reuse of essential resources, and fostering inclusion and well-being for all.
Mitsubishi Electric has been incorporating technology that enables greater electrification, automation, and sustainability in the home, office, or manufacturing facility into all of its product lines for more than 20 years.
For instance, Mitsubishi Electric Trane HVAC US’s all-electric heat pumps in the home provide low- to moderate-income households with a way to qualify for incentives under the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (IRA), while also helping to clean up the environment and significantly lowering their utility bills due to increased energy efficiency.
Driving Efficiency and Sustainability with AI-Driven Data Sharing: Mitsubishi Electric’s Circular Digital-Engineering Approach
The company’s AnyMile Drone Management Platform aids in the coordination of drone-based logistics for the movement of goods (and ultimately people), bringing shippers, drone manufacturers, crane operators, and ancillary service providers onto the same platform to boost drone travel and trafficking efficiency and lessen the carbon footprint of such operations.
Gathering and centralizing data from now divergent systems and devices to drive process automation is essential in light of recent developments in machine learning and AI technology. M.E. long-term vision includes integrating products, services, and technologies across the different industries where they operate, keeping this driver in mind.
The creation of a cross-industry data gathering and management approach that will aggregate data from their offerings to share insights with their customers, enable ongoing evolution of products and services, and create value at the societal level is an essential component to realizing this vision.
In other words, Mitsubishi Electric is quickly evolving into a data provider.
M.E. uses a “Circular Digital- Engineering” concept across all of their global operations that makes use of powerful intra-business group connections and knowledge sharing to consolidate data, analyze it, and develop decisioning models to speed up business processes, add new value to customers lives, as well as contribute to the resolution of important cultural issues.
Driving Sustainable Innovation: Mitsubishi Electric’s Circular Digital-Engineering Approach in Action
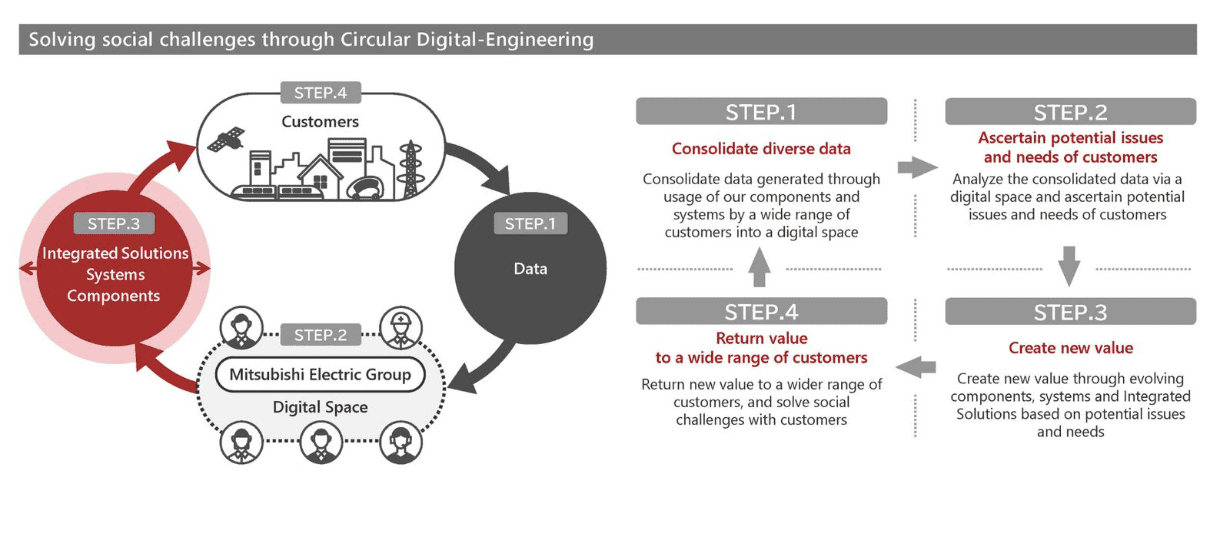
The idea calls for a four-step repeated process wheel:
1. Consolidate different data: Combine data produced by a variety of customers use of their systems and components into one online space, such as an online knowledge base platform.
The SUSTIE net zero energy building (ZEB) test facility operated by Mitsubishi Electric in Japan serves as an illustration of this data consolidation. The SUSTIE facility is a high-performance, connected, and sustainable smart building based on strategically captured real-time data that can be shared to optimize operations and functions. It is named after the combination of “sustainability” and energy.
The ICONICS automation software in the building is used by SUSTIE’s dynamically connected bright systems to gather, share, analyze, and act on aggregated system data. ICONICS, a Mitsubishi Electric group company, has hundreds of thousands of similar installations spread across more than 100 nations. One notable use case is the Zentrum für Psychiatrie Südwürttemberg (Center for Psychology) in Germany, where the automation software helps save energy and enhance occupant comfort in the center’s 157 buildings, which provide expert mental health care and patient treatment.
2. Ascertain potential problems and customer needs: In this step, M.E. works closely with their clients to analyze and model private, multi-dimensional datasets from their product and solution installations in order to identify problems, better understand their needs, and find new ways to improve operations or the business.
3. Develop new value by modifying components, systems, and included solutions across business groups that are based on data-driven potential issues and needs.
4. Return fresh value to a wider range of customers: Work with customers to address social issues.
This four-step procedure has produced a constant feedback loop that causes all Mitsubishi Electric business groups to regularly innovate, along with partners who have complementary goods and technologies. Government or quasi-government organizations, as well as utilities that aim to advance the viability of bright societies, can be among these partners.
Their Smarter Grid Solutions distributed energy resources (DER) management software products, which enable power systems anywhere in the world to effectively manage their DER assets and evolve toward carbon-neutral, Net Zero energy operations, are another example of the Circular Digital- Engineering concept in action. Real-time data is used in this software to track and optimize power grids and energy systems with numerous distributed, fresh, and versatile energy assets, including hydroelectric, wind, solar, as well as other energy-related assets like energy as a service and grid capacity management.
One of the few businesses in the world that offers a wide range of goods, services, and technologies to assist governments and businesses promote sustainability, hasten decarbonization, or enhance the quality of life for people worldwide is Mitsubishi Electric.
M.E. will keep integrating data across their various products and business services over the ensuing decades. Mitsubishi Electric will be at the forefront of a truly green, world smart society thanks to their expertise in data analytics, AI, and decision-making derived from their Circular Digital-Engineering model and use of people-centric technology.