The European Commission has developed the Common Agricultural Policy 2023 ( CAP 23 ) legislation to provide European farmers with support through disasters, environmental support, and financial support as farmers become more and more concerned with both the environment and the industry.

CAP 23 – 27: Advancing the European Green Deal through Sustainable Farming and Climate-focused Policies
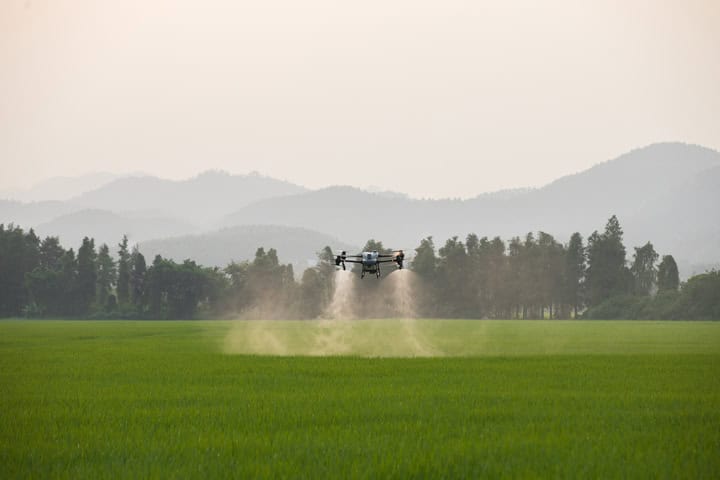
CAP 23 strives to be the most economically and climate-focused CAP to date, a greener approach. To receive full payments, farmers are required to meet an improved set of standards covering the environment, climate, food safety, plant protection products, animal welfare, and working conditions. This conditionality principle is applicable to nearly 90 % of the EU’s agrarian landmass, highlighting the importance of mainstreaming sustainable farming practices.
The Plans allocate a major 32 % of the CAP budget, or roughly €98 billion, to deliberate actions in support of climate goals. For instance, Italy designates over €10bn for climate and environmental interventions, compensating farmers for adopting practices that are more socially and climate- helpful. These include the use of fertilisers and pesticides, for example, or soil conservation practices.
These efforts help to demonstrate CAP’s commitment to promoting biodiversity and climate sustainability while encouraging farmers to adopt more sustainable practices.
Balancing Agricultural Income Support and Sustainability Initiatives for Rural Development
Agriculture income only accounts for 45 % of the national average wage in the country, with variations between the agricultural sectors and farming systems. In 2020, CAP support accounted for 23 % of EU farm income on average. It proves crucial in preventing rural depopulation and land abandonment, as well as preserving agricultural activity and jobs in isolated rural areas.
To receive full CAP payments, farmers must respect an improved set of requirements and standards for the environment, climate, health, animal welfare, and good working conditions. This conditionality principle is applicable to close to 90 % of the EU’s agricultural landmass and plays a significant role in mainstreaming sustainable farming practices.
Fostering Remote Community Development and Employment through Innovative Agricultural Initiatives
Beyond income support, the CAP makes significant contributions to remote community development and employment creation in both upstream and downstream agricultural sectors.
With a dedicated focus on the social and financial fabric of EU remote areas, CAP 23 invests in precision farming, innovation, and farmer training across the EU.
In concrete terms, CAP allocates nearly €25bn (8% of the total budget from 2023 to 2027), significantly boosting the economic landscape of EU rural areas. Initiatives like installation aid and higher investment rates aim to attract 377, 000 fresh young farmers, fostering innovation and job creation in the inland agricultural sector.
However, we aim at having 377, 000 new young farmers during this programming period, thanks to many tools such as the support income for young farmers, the installation aid for young and new farmers, higher rate for investments, support to farm transfers via the co- operation tool, or even intergenerational exchange of knowledge.
Beyond agrarian activities, the CAP framework provides a number of opportunities to support rural areas in creative ways. Numerous Member States make use of these resources to promote business creation in fields other than farming, including social services, healthy parks, clean energy production, rural mobility systems, and other types of economic development.
The Horizon Europe fund, with over €3bn, supports research and innovation in agriculture, forestry, and remote areas, and provides a significant financial backing for technological advancements, creating job opportunities in downstream sectors.
Strategic partnerships, like Circular Bio- based Europe, showcase a dedication to job creation and economic protection. Precision farming techniques, supported by CAP, increase crop yields, increase productivity, and create jobs in related industries.
In summary, the multi-faceted approach of the CAP constantly promotes remote community development and employment across the whole agricultural value chain.
Ensuring Accountability and Transparency: Monitoring CAP Funding and Implementation for EU Budget Safeguarding
To safeguard the EU budget and ensure that every dollar is spent, the Commission has put in place sound rules and procedures.
EU countries are in charge of implementing and controlling the different schemes under the CAP legislation under shared management. The Commission’s job is to make sure that Member States effectively manage CAP funds, that taxpayers ‘ money is spent properly, and that the EU does not pay for projects or claims that go against the established standards.
Farmers and different beneficiaries are paid for in EU countries through local or national paying bodies, which carry out a rigorous system of checks before being paid.
Additionally, the Commission audits its systems several times a year and asserts that the Commission has been held accountable for any errors or, more often, fraud that have resulted in the payment of EU rules.
The Commission has already released a first evaluation report in November 2023, which evaluates the impact of the Strategic Plans to meet the goals of the Common Agricultural Policy ( CAP ) 2023-2027, particularly those that are related to the environment, climate, and societal expectations like animal welfare.
The CAP Strategic Plans, according to the report, aim to deliver the most optimistic CAP always from an environmental and climate perspective.
There will also be yearly performance reports and time and last evaluations in 2026 and 2031, both. In line with its transparency and monitoring requirements, the European Commission even provides detailed information on all CAP Strategic Plans online, with a summary of all Plans, a catalogue of CAP interventions, and dashboards on result indicators and economic allocations.