Rare earths, a collection of seventeen elements with chemical similarities, are essential to the development of the contemporary world.
Due to their distinctive electrical and luminous properties, they are essential to many industries, including technology, solar energy, and defense.
They are utilized, for instance, in the production of wind turbines, electric vehicles ( EVs ), and computer hard drives. It is crucial to comprehend the state of the world’s unique earths today.
Due to technological advancements and a greater emphasis on alternative energy solutions, the predicted demand for these elements is anticipated to increase tremendously over the next ten years. But, this brings up a number of worries, including supply chain issues and the negative effects of mining and processing these elements on the environment.
The global outlook for rare earths is provided by Innovation News Network, including information on production distribution across nations, potential replacements for these elements in different applications, and the economic effects of their extraction and processing.
What are the primary applications of unusual earth elements in contemporary significant industries?
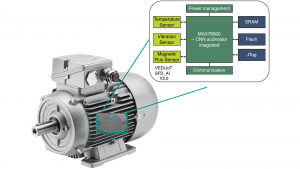
Rare earth elements play a crucial role in the world of crucial industries, especially the burgeoning technology sector, by being used as vital parts in various applications, including computer hardware and electric vehicles.
These materials ‘ chemical characteristics contribute to their common use in a variety of industries. For instance, neodymium is used to create high-performance lasting magnets, which are essential for electric motors in hybrid cars and hard disk drives in computers. Similar to this, europium’s unique ability to emit red light when exposed to electric impulses has made its use in computer monitors and television screens possible. Additionally, rare earths like yttrium and samarium are greatly used in defense applications to enhance the performance of radar systems and precision-guided weapons.
In addition to these applications, health technologies also profit from some rare earth elements ‘ special qualities. Prometheus is used as a source of radiation for cancer treatment, while gadolinium is frequently used in magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI ).
In terms of space exploration, celestial regolith samples recovered by Apollo missions have found remnants of rare earth elements, suggesting their potential usefulness outside of Earth-bound applications.
However, according to their dispersed geographic distribution and intricate extraction processes, sourcing these priceless resources presents a number of innovation challenges.
Despite this, progress is being made toward securing green supplies for upcoming technological advancements thanks to ongoing research into other mining techniques and recycling techniques.
In the upcoming ten years, what is the anticipated demand for unique earths?
Due to their important role in high-tech industries and alternative energy solutions, projected demand for rare earths is anticipated to increase tremendously over the next ten years.
Rare earth elements play a crucial role in the technology that shapes our present world, serving as essential components in cutting-edge electronics, EVs, wind farms, and solar panels. Strategic reserves of these elements are being sought worldwide in response to the rising demand, which has a significant impact on trading dynamics and creates new investment opportunities.
Overall, it becomes clear that green management strategies must be adopted immediately while even enhancing exploration initiatives to ensure future availability given the crucial role played by these important resources in several sectors combined with impending scarcity issues.
Which nations produce the most unique earth elements?
Over 70 % of the world’s total output of rare earths is currently produced by China, followed by Australia and the United States.
China’s dominance in REE production can be attributed to superior Element Extraction Techniques that have been perfected over time and less restrictive regulations than other nations. However, due to REEs ‘ crucial role in a variety of industries, from technology to defense, this monopoly has an impact on international trade that can be felt all over the world.
Due to their geographic dispersion and intricate processing requirements, REEs ‘ extraction process and distribution present the main supply chain challenges. Despite these obstacles, there are sizable investment opportunities for countries prepared to enter this industry as the demand for goods rises.
Each nation faces particular difficulties that have an impact on both its capacity and the global supply chain and trade dynamics involving unusual earth elements.
What could be used in different applications in place of unusual earth elements?
A promising way to reduce reliance on these limited resources is to look into possible alternatives to using unique earth elements in various applications. To find worthwhile replacements, it is essential to conduct a thorough replacement assessment while taking into account their availability, cost-effectiveness, and climate effects.
Certain materials, such as cerium oxide, have been replaced by polymeric metal alloys or chemical processes that do not call for such elements as a result of innovations in alternatives.
Another illustration is the switch from unique earth-free magnetite or induction magnets to neodymium magnet types, which are frequently used in wind turbines and electric vehicles. It’s important to keep in mind that these substitutes frequently have their own set of complex restrictions and difficulties.
Analyzing the financial ramifications of switching to substitutes is also crucial because the original costs associated with technology development or production process scaling may be higher. When assessing financial viability, the price volatility of unusual earths also adds a new layer of complexity.
While some alternatives may seem plentiful right now in terms of supplement availability, anticipated demand may present supply risks in the future.
Are there any policies in place to reduce the economic effects of mining and processing unique earth elements?
The mining and processing of rare earths have a significant negative impact on the environment, causing everything from biodiversity loss to soil erosion and water contamination. Chemicals are frequently used extensively in extraction techniques because they have the potential to leach into the environment and harm flora and fauna.
Additionally, the dangerous nature of uncommon earth’s tailings continues to present a major challenge for waste management. Governments around the world are struggling to strike a balance between financial gains from mining and biological conservation due to these environmental hazards, which present serious regulatory challenges.
At the national and international levels, policies for green mining are being developed, but because local regulations and community impact factors vary by region, enforcement is still uneven.
In order to develop comprehensive strategies that properly address these urgent climate issues while also ensuring the continuing supply of worldwide rare earths, which are essential for many industries, it is essential that all stakeholders, including governments, industry players, and communities affected by mining, engage in meaningful dialogue.