Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining widespread attention for their environmental benefits, cost savings, and innovative technology. However, Select Power Systems explores both the benefits and challenges related to EV charging infrastructure, a key factor in widespread EV adoption. EVs provide significant savings on fuel and maintenance, while reducing greenhouse gas emissions as the energy grid shifts to cleaner sources. Despite these advantages, challenges such as range anxiety, charging infrastructure gaps, and charging time delays hinder the broader adoption of EVs. Range anxiety remains a major issue, with long-distance travel requiring careful planning for charging stops. Although public fast chargers are expanding, rural areas still face a shortage, and charging times at stations remain longer compared to traditional refueling. Additionally, EVs place a strain on the electrical grid, especially during peak charging times, raising concerns about grid stability. Smart grid technologies, time-of-use pricing, and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems can help mitigate these issues, but require further investment and coordination. As battery technology and charging infrastructure improve, the cost of EVs will likely decrease, making them more accessible to the general public. Overall, the ongoing efforts to develop EV charging infrastructure will be crucial to ensuring a green, sustainable future.

The future holds in electronic vehicles, but what stops them? Select Power Systems explores EV charging infrastructure, highlighting benefits and areas requiring improvement.
Electric vehicles ( EVs ) have attracted a lot of attention in recent years due to their potential environmental advantages and technological advancements. Let’s look at the benefits and drawbacks of electric vehicles, as well as their effects on charging facilities and the energy grid.
A wealth of benefits
EVs have many benefits, including considerable savings on fuel costs. The majority of charging takes place immediately at home, where electricity costs are typically lower than gasoline. Yet people hard chargers, while more costly than home charging, are also cost-effective compared to traditional fuelling.
Another benefit of electric motors is that they can accelerate more quickly from a standstill thanks to their instant torque. High-performance EVs, such as the Tesla Model S and Porsche Taycan, exemplify this, with perhaps popular EVs like the Chevrolet Bolt EV offering amazing acceleration.
As the energy sector transitions to cleaner sources, EVs become yet more eco-friendly. EVs do n’t emit tailpipe emissions, which leads to cleaner air and lessening greenhouse gas emissions.
In addition, EVs have fewer moving parts than internal combustion engine ( ICE ) vehicles, leading to reduced maintenance costs. No oil changes, fewer brake replacements, and streamlined drivetrains contribute to long-term savings.
Challenges facing common adoption
Range anxiety
There are a number of issues that need to be addressed in order to make electric vehicles ( EVs ) a more affordable long-term option. Despite improvements, EVs also have limitations when it comes to range.
While some models have more than 300 miles of range, long trips still demand careful planning and stop-and-go charging. Because you need to find charging stations and allow for more time to travel to your destination, this can cause issues with more routes.
Although addressing range anxiety is still important for widespread adoption, utilities can make plans for it by monitoring EVs using smart meters and model grid-up scenarios.
Improving EV charging infrastructure
Another issue is with charging infrastructure, and expanding infrastructure is crucial to EVs ‘ future success. While billions are invested in common charging networks, gaps persist. Rural areas and some places lack enough charging stations.
As charging infrastructure needs improvement, but does the time it takes to charge at these stations. Public quick chargers can take more than refueling at a gas station, despite being suitable for home use. A challenge is to balance more quickly with grid stability when charging at the same speed, and faster chargers are required for a time-saving benefit to be realized.
Addressing affordability
Given the current state of the economy, vehicle prices, including those of EVs, have risen, making them unaffordable for some people. While there are long-term savings on fuel, maintenance, and, in some places, also a tax break for owning an EV to offset the initial investment, these savings are minimal compared to the cost of what we need in the infrastructure itself. But, as production scales up and battery technology improves, prices are expected to equalise.
Grid strain
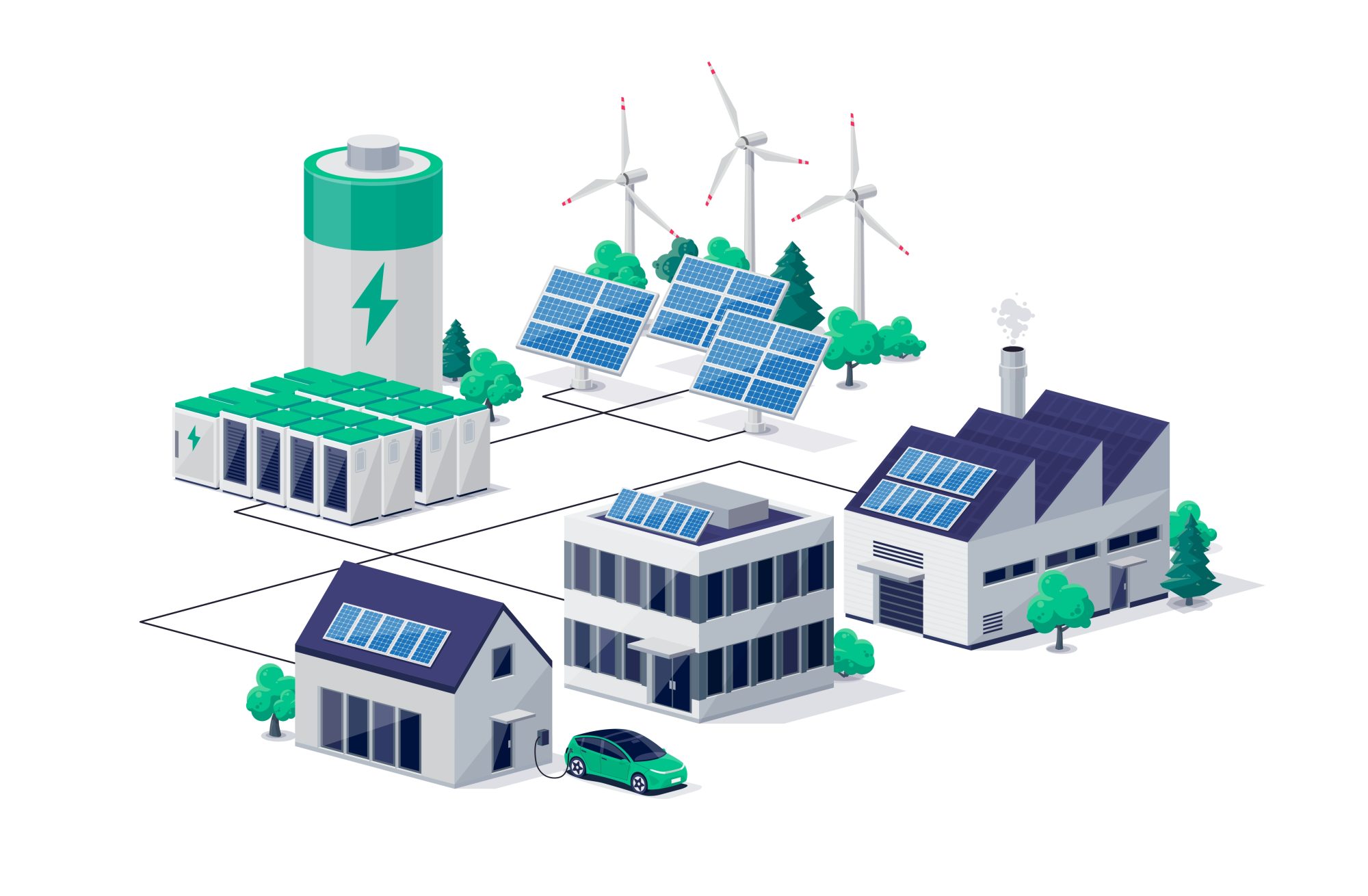
One of the main issues with EVs and their charging stations is how they affect the energy grid. EVs put a lot of pressure on the electrical grid, especially at peak charging times, which strains utilities and costs money to upgrade the grid. In addition, the operation of EV charging stations can cause harmonics to enter the grid, which can have an impact on power quality.
But, smart grid technologies, time-of-use pricing, and managed charging can mitigate these challenges. Coordinated charging, vehicle-to-grid ( V2G ) systems, and renewable energy integration will shape the future of EV-grid interactions. This, once, takes time, money, and ongoing collaboration between utilities and governments.

A worthwhile task
In conclusion, EVs offer powerful advantages, but challenges remain. Although time and money are substantial obstacles, the ongoing efforts to install charging stations wherever necessary increase employment opportunities and should boost the economy. The transition to cleaner energy sources is still essential to maximize EV benefits while minimizing their impact on the grid.
The transition to electric mobility will accelerate as technology develops and the infrastructure grows, helping both consumers and the environment as we strive for a green future.