Wi-Fi has become a technology for investing in, according to Michael De Nil, CEO and co-founder of Morse Micro.
While Wi-Fi 7 garners attention as the newest and fastest Wi-Fi technology, the evolution of the Internet of Things (IoT) brings Wi-Fi CERTIFIED HaLow into the spotlight—a Wi-Fi standard designed to meet the connectivity needs of an expanding global IoT ecosystem, expected to burgeon to 27 billion devices by 2025, according to IoT Analytics.
Wi-Fi HaLow, poised to transform different environments ranging from bright homes to urban landscapes, offers strong, far-reaching, and energy-efficient wireless connectivity solutions essential for the IoT’s transformative era. Here’s everything you need to know about Wi-Fi HaLow.
What is Wi-Fi HaLow?
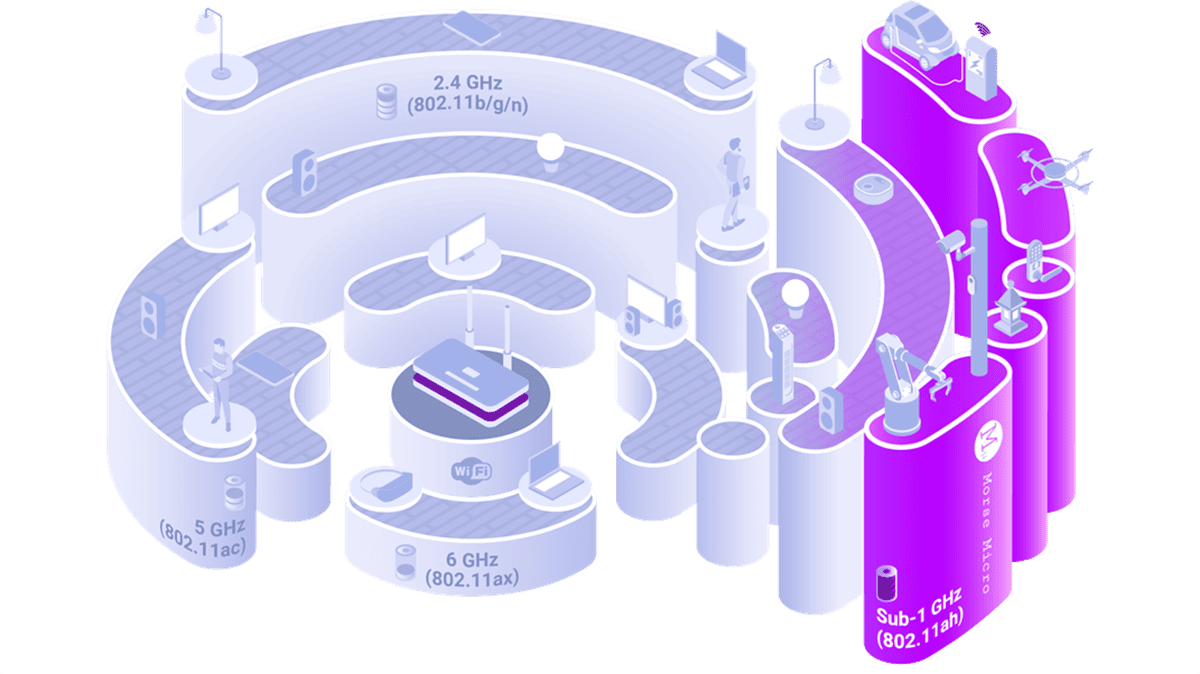
Wi-Fi HaLow, based on the IEEE 802.11ah protocol and introduced in 2016, operates on sub-1GHz frequencies, different from the standard 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6 Billion frequencies used by Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 6E, and Wi-Fi 7 protocols.
In line-of-sight scenarios, Wi-Fi HaLow can provide connectivity over greater distances by supporting connections up to three kilometers and beyond, and it can also penetrate deep materials with its narrowband signals. Wi-Fi HaLow properly addresses important IoT issues like expanded range and lower power consumption, despite its use of lower frequencies, which results in narrower channels and lower bandwidth (yielding data rates from 150 Kbps up to 86.7 Mbps depending on the distance ).
In field tests, Wi-Fi HaLow’s long-range capabilities have been demonstrated, including a remarkable demonstration in San Francisco’s Ocean Beach, which demonstrated a coverage area that is 100 times greater than that of normal Wi-Fi networks.
Wi-Fi HaLow is not intended to replace or enhance conventional Wi-Fi standards. It extends connectivity over longer distances without the need for specialized hubs, several access points, or complicated wired connections, making it especially helpful for IoT devices, smart city projects, and mesh networking.
In the US, Wi-Fi HaLow operates in the 900 MHz frequency range within the license-exempt sub-GHz spectrum, allowing complimentary use for everyone. Globally, Wi-Fi HaLow may use various sub-GHz frequencies depending on local regulations and accessible spectrum, adapting to numerous worldwide settings.
What distinguishes Wi-Fi HaLow from conventional Wi-Fi?
While conventional Wi-Fi protocols, such as Wi-Fi 5, 6, and 6E, have focused on maximising wireless speeds and reducing overhead, they often fall short in signal range. Wi-Fi HaLow addresses this limitation, enhancing connectivity particularly in IoT environments where devices require trusted, long-range connections.
Wi-Fi HaLow is able to penetrate barriers and provide considerably better transmission range than traditional Wi-Fi bands like 2.4 GHz, 5G Hz, and 6 GHz because it operates in the sub-GHz frequency spectrum. This feature is essential for IoT devices that are distributed across a range of settings, from factory floors to corporate campuses.
Moreover, Wi-Fi HaLow is designed with power efficiency in mind. It supports advanced power management capabilities like Restricted Access Window (RAW) and Target Wake Time ( TWT), which enable devices to operate for an extended period of time in a low-power state. This capability is necessary for battery-operated devices like mobile sensors and security cameras, so they can function for years without having to replace the batteries.
What about Matter, Thread, Z-Wave or Zigbee?
Wi-Fi HaLow is not the first technology to offer connectivity for IoT devices. Other technologies such as Z-Wave, Zigbee, Thread and Matter even play important roles in the IoT landscape, each with different advantages and limitations.
Z-Wave shares similarities with Wi-Fi HaLow, using sub-GHz frequencies for longer range and lower power consumption. But, while Z-Wave’s Long Range version, introduced in 2020, increases its network capacity to 4, 000 devices and matches HaLow’s signal range, it also falls short of HaLow’s capability to support up to 8, 191 devices. Also, Z-Wave requires a main controller to manage network operations successfully.
Zigbee operates across different frequencies, including 780 MHz, 868 MHz, 915 MHz, and the typical 2.4 GHz band, providing faster data transfer rates but with limited range. Despite having more than 65, 000 nodes in its network, Zigbee struggles with interoperability and security issues, and it also needs a coordinator to manage its networks.
Thread, a newer low-power protocol, operates only at 2.4 GHz and is IP-based, allowing devices to connect without the need for a hub. It only supports about 250 devices, making it less suitable for large or high-bandwidth applications like security cameras, and requires a Fabric border router for internet connectivity.
In contrast to these technologies, Wi-Fi HaLow excels with its huge reach, strong security, and large device capacity, all without the need for more infrastructure such as hubs or controllers. Wi-Fi HaLow, which operates in the underused sub-GHz band, reduces congestion in bands that are used by conventional Wi-Fi and another IoT protocols, resulting in more accurate and comprehensive coverage. This capability makes Wi-Fi HaLow particularly efficient for a wide range of IoT applications, from bright cities to business environments, where smooth, broad connectivity is important.
Wi-Fi HaLow combines Matter technology with its capabilities, which likewise keeps up with the most recent trends in IoT networking, allowing devices from various ecosystems to communicate without interruption, thereby reducing costs and facilitating adoption.
What are the benefits of adopting Wi-Fi HaLow?
Wi-Fi HaLow is working to increase cellular connectivity in a variety of IoT use cases, including intelligent factory and warehouse environments, smart home ecosystems, and enterprise campuses with considerable cellular networks for access control and security cameras. Traditional 2.4 GHz wifi bands are now overcrowded, simply allowing three non-overlapping channels, which frequently causes significant network congestion and uncertain operation in mission-critical IoT scenarios.
In contrast, Wi-Fi HaLow operates on the underutilised sub-GHz spectrum, providing more than 26 non-overlapping channels. Yet in environments with thousands of connected devices, this significant increase in the number of available channels significantly lowers the risk of interference and congestion.
Also, Wi-Fi HaLow’s extended range capabilities enable a single access point to essentially cover large environments. This enables the provision of long-range, trusted internet connections for both indoor and outdoor devices using a single router or mesh system. This arrangement is effective for both homes and businesses, ensuring trusted connectivity to exterior sensors, security cameras, and other IoT devices in places like gardens and guest houses. It also ensures high-bandwidth devices inside the main building. Wi-Fi HaLow’s considerable coverage makes it easier to install several mesh nodes and Wi-Fi extenders, thereby reducing overall infrastructure costs and simplifying network setup.
How to deploy Wi-Fi HaLow technology in IoT Connectivity ?
Adopting any new generation of Wi-Fi, including Wi-Fi HaLow, requires agreeable infrastructure. To benefit from the Wi-Fi HaLow specification, both the wireless router and the related devices must support it. Although Wi-Fi HaLow has experienced a slow adoption rate, the development of technology is fast-approaching, and an increasing number of devices are anticipated to support this specification as the development progresses.
Numerous manufacturers have developed Wi-Fi extenders that incorporate Wi-Fi HaLow technology, which can extend cellular connectivity to hundreds of meters, to broaden the reach of already-established networks. For instance, at CES 2024, Abode unveiled its new Edge security camera, which uses Wi-Fi HaLow and is slated for release soon at approximately $200.
But, it is important to keep in mind that to gain access to the advantages of this technology, new hardware is required in order to upgrade existing wireless routers or devices to Wi-Fi HaLow via firmware updates. This requirement mirrors the Wi-Fi 6E to Wi-Fi 7 build process, which calls for the use of new hardware.
Will Wi-Fi HaLow Succeed?
Wi-Fi HaLow is poised to transform the IoT connectivity landscape, but as with any innovation, the journey is continued. While the potential benefits of Wi-Fi HaLow are huge, real-world applications and widespread adoption will be the supreme tests of the protocol’s success. The Wi-Fi CERTIFIED HaLow logo has obvious value; it identifies a device’s ability to easily connect over longer distances, pass through difficult barriers, and operate with thousands of devices at once—qualities that are necessary in settings ranging from intelligent homes to industrial complexes.
With its robust security measures, outstanding performance standards, and proven reliability, Wi-Fi HaLow is now meeting the high expectations end users have for modern IoT applications. As Wi-Fi HaLow continues to integrate into existing IoT ecosystems, its ability to deliver optimum performance in a range of circumstances is becoming more and more apparent. Users are finding that Wi-Fi HaLow maintains great performance while also allowing compatibility with existing Wi-Fi infrastructure. This flawless integration and trusted operation demonstrate Wi-Fi HaLow’s readiness to meet the demanding and expanding needs of the IoT landscape.