An overview of the continuous EU-funded project “LH2CRAFT” which focuses on the safe and effective transport of large amounts of liquid hydrogen in large quantities.
Transport is a cornerstone of both the European Union’s inside cohesion and its global trade, driving economic growth, employment, and social equality. However, as the world’s reliance on transportation has deepened, the same has applied to its environmental impact.
World transport challenges and opportunities
Transport activities ‘ carbon footprint has risen to alarming levels. The bad climate, safety, and congestion issues of transportation, as well as their unequal access to users, are at undesirable levels, according to the European Investment Bank‘s Transport Lending Policy 2022.
In response, the European Green Deal Strategy has set a bold target of a 90 % reduction in transport emissions, compared to 1990 levels, by 2050, achieved through the adoption of more sustainable, affordable, accessible, healthier, and cleaner alternatives.
The global energy crisis, which began much before Russia invaded Ukraine, is what is exacerbated by this issue. Europe’s energy woes are simply getting worse as a result of the conflict, with the continent facing a looming winter with diminishing energy reserves and much chance of recovery. Due to lower business activity leading to lower energy demand, the pandemic partially obscured these energy security issues. The energy security is becoming more evident as the economy recovers, creating what some people call the perfect storm.
However, amidst these challenges lies a major opportunity. Decarbonization initiatives are becoming more popular, with both governments and businesses acknowledging the ability for transformational change. Leading companies like Maersk have committed to carbon-neutral operations by 2050, while MSC and France’s CMA CGM are investing heavily in carbon-neutral shipping technologies.
The energy that drives these efforts is concentrated on liquid hydrogen ( H2 ), a fuel with the highest mass per mass of any fuel. However, its small ambient temperature density poses a challenge. Because the liquid hydrogen must be transported from production sites to areas with high demand, it requires sophisticated storage and transportation options to enable its use over extended distances.
In this context, the LH2CRAFT project is pioneering a new generation of sustainable, commercially attractive, and safe technologies for the long-term storage and long-distance transportation of liquid hydrogen ( LH2 ) on ships. A 180m3 containment system serves as the project’s demonstration model, and it is the goal of the project to create innovative storage solutions that can operate at temperatures as low as 20 K (-253°C ).
By advancing these technologies, LH2CRAFT not only addresses cultural energy needs but also strengthens the EU’s leadership in global maritime innovation. The project is expected to significantly impact Europe’s innovation-driven industry, creating highly qualified jobs, delivering useful scientific solutions, and setting global regulatory standards.
LH2CRAFT project outline and objectives
LH2CRAFT is a permanent Research & Innovation project that is primarily funded by the EU’s Clean Hydrogen Joint Undertaking, receiving funding from UK Research Innovation ( UKRI ) for the UK-based partners as well as contributions from the private sector. The project was the sole proposal that was awarded by the EU within the Call for Proposals ( HORIZON-JTI-CLEANH2-2022-02-06: ‘ Development of large scale LH2 containment for shipping.’

The project is coordinated by the Greek-based business HYDRUS ENGINEERING SA, a worldwide engineering company that provides complete and integrated solutions for the defense, energy, and maritime industries.
The project’s primary goals are summarized as follows:
- Ensuring the safe, cost-effective, and energy-efficient storage and transportation of large quantities of liquid hydrogen ( LH₂ ) over long distances.
- Creating a cargo containment system ( CCS ) for LH2 shipping that is larger than the size restrictions of the aquatic sector’s most recent technological advancements.
- designing a LH2 storage system that is both flexible and adaptable, with dimensions comparable to those of existing LNG ( Liquid Natural Gas ) carriers.
- Securing Approval in Principle ( AiP ) and General Approval ( GA ) for the CCS, as well as AiP for the auxiliary systems, from ABS IACS Classification Society ( partner of the consortium ).
- Demonstrating the viability of the CCS through the extensive design, construction, and validation of a reduced-size prototype with a capacity of 180m³.
- developing a detailed cost estimate as well as a safe and revolutionary theoretical integrated ship design.
- By promoting the development of highly qualified jobs, developing effective scientific solutions, and establishing international regulatory standards, the European Union is strengthening its position as a global maritime leader, which benefits both industry and society.
The project’s expanded and thorough series of testing activities covers everything from subsystem performance verification to material characterization under cryogenic conditions.
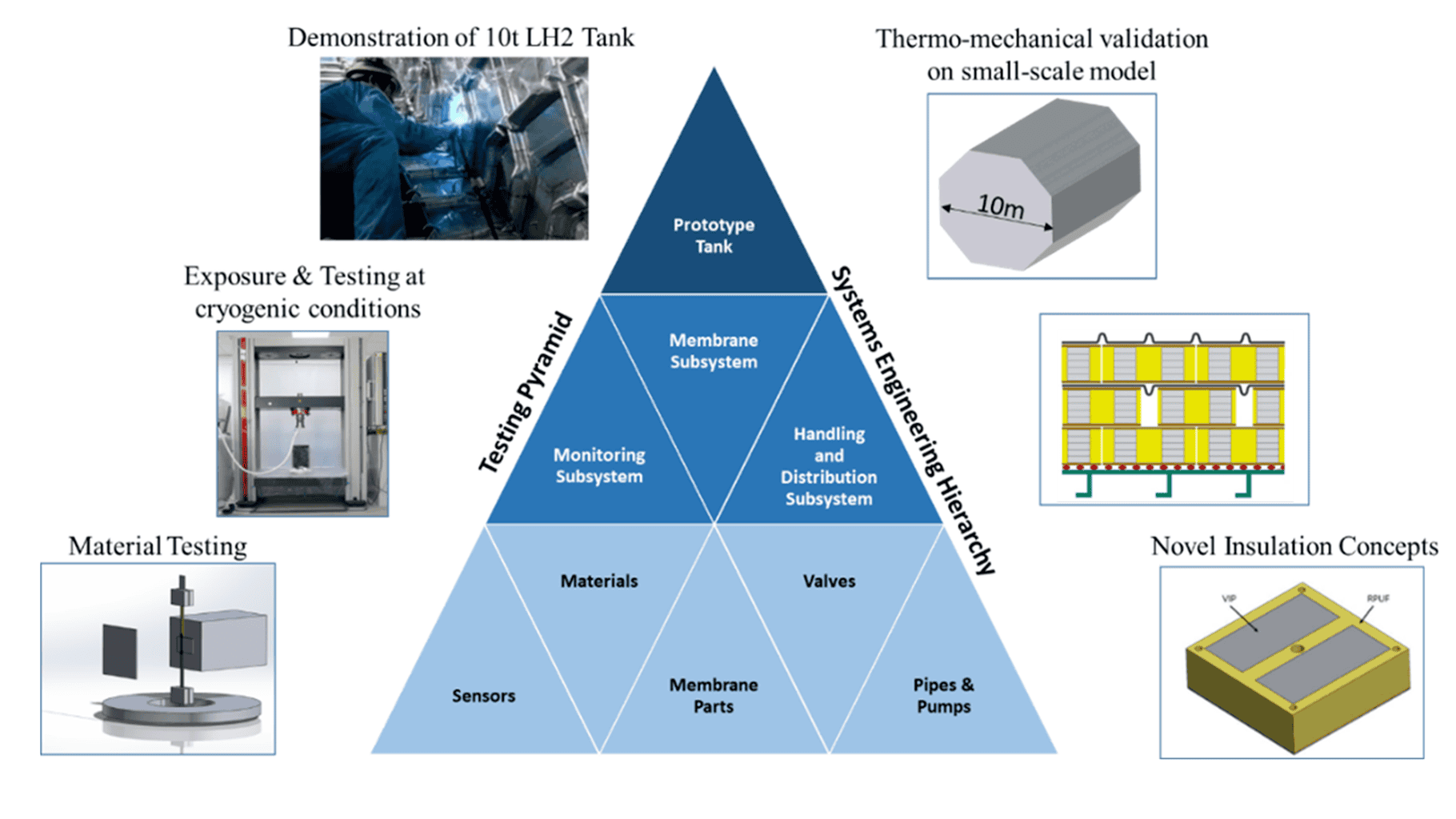
LH2CRAFT in numbers
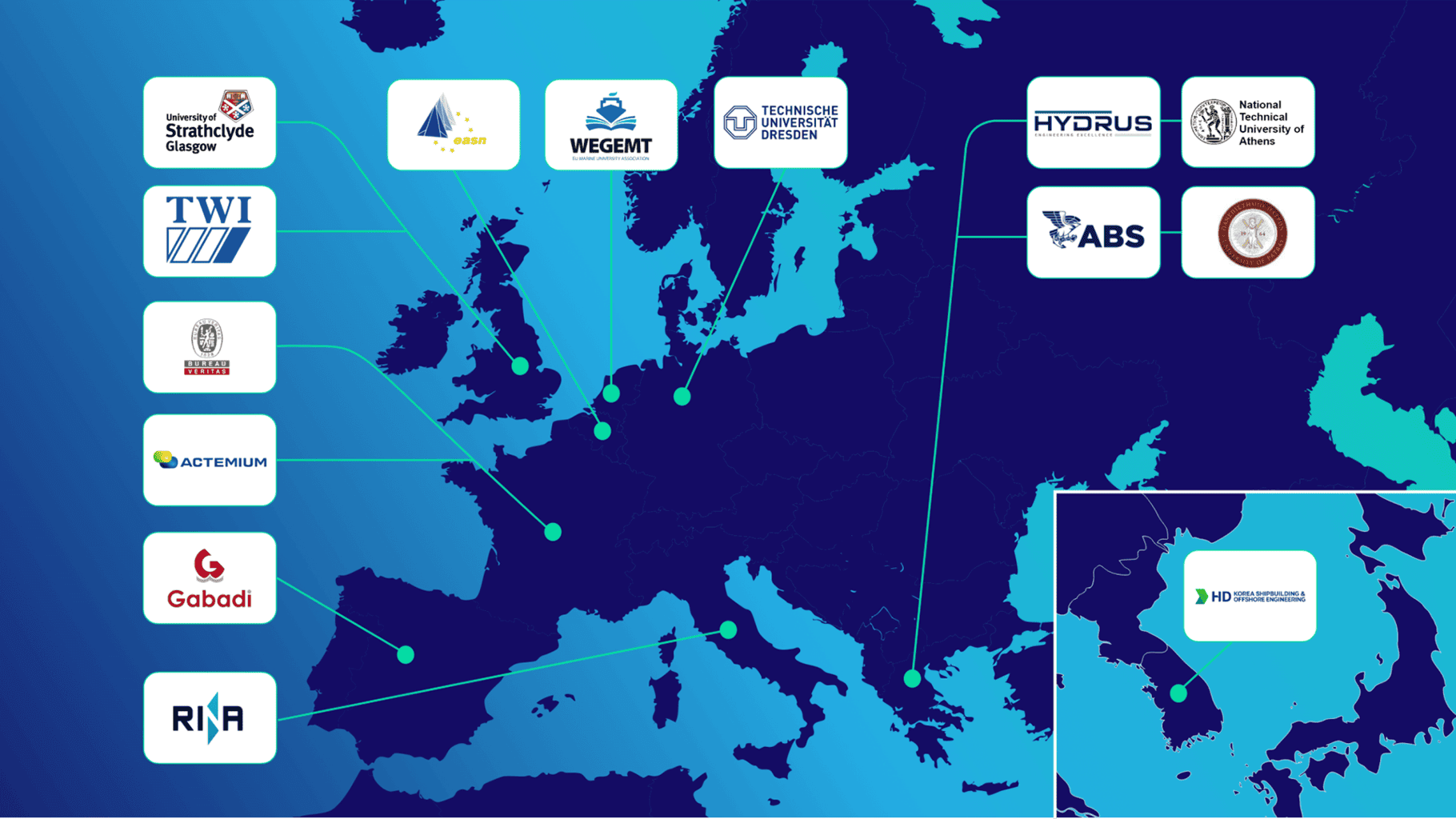
The LH2CRAFT project, initiated in June 2023, is a 48-month endeavour. It is a cooperative effort of 14 partners from nine countries, comprising a consortium of engineering consultants, educational institutions and research organisations, IACS classification societies, and business partners.
More specifically, the following partners ‘ categories are working together in a coordinated way to successfully carry out the project and accomplish its main objectives:
- Major Classification Societies / IACS Members: ABS ( American Bureau of Shipping – Greece ), RINA ( Registro Italiano Navale – Italy ) BV ( Bureau Veritas – France )
- Technical Universities: TUD ( Technische Universiteit Dresden – Germany ), NTUA ( National Technical University of Athens – Greece ), UOS ( University of Strathclyde – UK), UPAT ( University of Patras – Greece )
- Industry Partners: HYD ( Hydrus Engineering SA – Greece ), HD KSOE ( HD Korea Shipbuilding Offshore Engineering – Republic of Korea ), GBD ( Gabadi – Spain ), ACT ( Actemium– France ),
- Research Organisations Network Associations: TWI ( The Welding Institute – UK), WEGEMT ( European Association of Universities in Marine Technology and Related Sciences – the Netherlands ), EASN ( European Aeronautics Science Network – Belgium ).
The Clean Hydrogen JU provides the majority of the project’s total funding at about €7.7 million ( 5.6% ). The UKRI ( €800,000 ) and HD KSOE, one of the largest shipyards in the world acting as the partner for the CCS design, provide the remaining funding.












