Utilize smart city advancements in waste management and air quality monitoring to explore the future of urban living.
The idea of the” smart city” has emerged as a cutting-edge method for urban planning and development, incorporating several strategies aimed at enhancing sustainability, service efficiency, and quality of life. Smart waste management and air quality monitoring systems, which use cutting-edge technologies to maximize resource use, lessen economic impact, and protect public health, are two of these tactics. These systems represent significant improvements in our ability to successfully manage urban environments.
Bright air quality monitoring, in particular, enables real-time detection and tracking of a variety of pollutants, from ground-level ozone to particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide, that can harm human health or contribute to climate change.
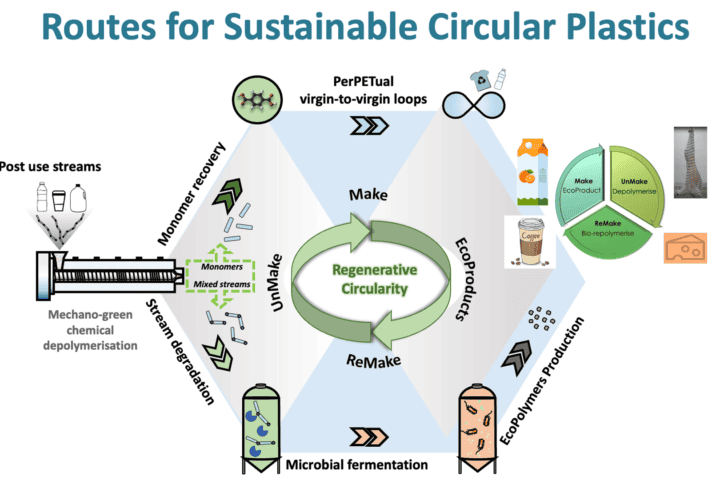
Smart waste management, which uses technology to streamline waste collection procedures, also creates opportunities for recycling and various types of recovery within the round economy model. Collectively, these two elements make up a crucial component of smart city infrastructure that aims to improve urban resilience and sustainability.
Describe a smart city.
An urban area that combines various digital and electronic information technologies into infrastructural elements to improve sustainability and the quality of life for its residents is referred to as a” smart city,” or” a metaphorical beacon of technological advancement.”
The foundation of these clever cities is made up of important elements like urban connectivity and digital infrastructure.
The goal of industrial connectivity is to build a network that is interconnected and allows for seamless data flow between people, things, and systems. However, in order to extract valuable insights from the vast amounts of data generated in a city, digital infrastructure entails implementing cutting-edge technologies like Internet of Things ( IoT), Artificial Intelligence ( AI), and Big Data Analysis.
Energy efficiency and bright transportation are two key factors that considerably influence how a smart city is shaped. For instance, bright transportation uses technology-driven solutions to improve traffic flow management, lessen congestion, and reduce emissions, promoting environmentally friendly modes of transportation. This could involve real-time traffic updates using cloud-based software or sophisticated transportation systems like AI-powered automatic vehicles.

Another important factor is energy efficiency, which can be achieved through cutting-edge solutions like smart lighting systems that adjust brightness in accordance with ambient light conditions or smart grids that use sensors to optimize energy distribution based on demand patterns.
The powerful evolution of a smart city continues to depend on citizen participation. Through platforms like smart applications or online portals where residents can voice their opinions or report issues directly related to their community’s wellbeing and development, it involves involving residents in decision-making processes.
Additionally, city administrators can use this collective intelligence to develop better problem-solving or lawmaking strategies, resulting in a more flexible governance mechanism. A real smart city thus goes beyond simply being technologically advanced; it uses online innovation for lasting growth while ensuring increased citizen engagement for better municipal service delivery.
What kinds of pollutants are detected by bright air quality monitoring systems?
These cutting-edge systems can detect a variety of pollutants, including carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, fine matter, and volatile organic compounds, by utilizing the strength of sophisticated technology.
Sensors that react to the natural or chemical characteristics of the targeted pollutant are commonly used in smart air quality monitoring systems to identify pollutants. These detection techniques employ complex algorithms that identify distinctive patterns or signatures connected to each particular class of pollutant. This not only makes correct detection possible, but it also makes it easier to distinguish between the various atmospheric pollutants.
A crucial component of these intelligent air quality systems is the accuracy of monitoring. High-precision sensors and efficient data analysis methods that reduce errors and false readings are used to ensure it.
System maintenance, nevertheless, is crucial for maintaining this level of accuracy over time, just like it is for any other digital device. This essential maintenance procedure to ensure optimum functioning includes routine calibration checks, sensor replacements when needed, and software updates.
The use of bright air quality monitoring systems has significant policy ramifications. These systems act as a valuable resource for policymakers in developing effective climate policies by offering real-time and specific pollutant data. They enable tracking progress toward cleaner air goals set by local governments or international organizations everywhere while also assisting in identifying pollution hotspots in cities for targeted interventions.
As a result, they are crucial to the detection of pollutants as well as the development of strategies to enhance urban air quality.
What advantages does bright air quality monitoring offer?
Modern environmental pollution detection systems provide accurate and real-time data that can guide actions to reduce exposure and lessen health risks, which is especially beneficial in the area of public health.
These sophisticated air quality monitoring tools ‘ accuracy has significantly increased thanks to technological advancements, making it possible to precisely identify and quantify a variety of pollutants. These changes make it possible to react right away to any dangerous spikes in pollutant levels, which lessens the likelihood that residents ‘ health will suffer.
Typical monitoring also helps in the identification of long-term patterns or trends that are essential for successful policymaking.
Another important benefit is community involvement; the display of real-time data on open platforms encourages citizens to become more aware of economic concerns. This transparency encourages people to actively take part in initiatives to improve air quality, like waste management programs or tree-planting campaigns.
Additionally, it creates opportunities for cooperation between decision-makers, academics, medical professionals, and the common public, all of whom stand to gain from better air quality.
So, the incorporation of intelligent air quality monitoring systems into industrial infrastructure represents a comprehensive strategy for promoting healthier communities rather than just an advancement in technology.
How does the circular economy benefit from intelligent waste management?
The proverb “turning trash into treasure” perfectly captures how digital waste disposal systems can support a round economy. Technology’s integration into waste management enables more efficient sorting, recycling, and repurposing of discarded materials, advancing the concept of closed-loop systems in which waste is a resource rather than an end product.
Like waste digitization has a wide range of effects, including lowering pollution, reducing landfill waste, conserving resources, and generating employment.
- Advantages of the spiral economy: By increasing resource efficiency and reducing environmental degradation, digital tools in waste management contribute to it. They make it possible to track waste streams precisely, which promotes better decision-making when it comes to disposal or recycling methods.
- Recycling innovation: New scientific developments have led to creative ways to manage various kinds of waste. For instance, while digital waste is excavated for precious metals, organic wastes can be turned into biofuels.
- Enhanced sustainability: Digitized waste management encourages energy conservation and carbon emissions reduction while lowering the demand for natural materials through higher recycling rates.
- Utilizing alternative energy: Waste-to-energy technologies transform non-recyclable waste into heat, electricity, or fuel, which lessens the need for fossil fuels.

Smart technologies ‘ contribution to changing how we handle trash is essential for both economic growth and social development, which are characteristics of green societies, as well as for environmental preservation.
It’s crucial to realize that achieving enhanced sustainability requires collective effort from all stakeholders – government bodies, private sector entities, communities, as well as individuals who generate waste regular — as we work to build better cities that are useful and eco-friendly. This includes actively taking part in appropriate source segregation, which makes recycling processes easier in the future and more advances round economy benefits.
Therefore, it is evident that incorporating electronic tools into our city’s infrastructure represents a major step forward in our quest to use renewable energy and create an environmentally friendly, long-lasting future.
What cutting-edge waste treatment methods are employed in bright cities?
The way waste is handled in metropolitan areas is being transformed by a number of ground-breaking technologies, which is assisting in the development of more responsible and productive communities. Waste sorting robots, which effectively separate various types of waste using machine learning algorithms and powerful sensor systems, are one example of this technology. By making sure that recyclable materials are effectively sorted and not contaminated with various types of waste, this not only increases waste management efficiency but also increases recycling rates.
Similar to this, brilliant bin systems with sensors assist in real-time trash monitoring and alert users when they need to be emptied, optimizing collection routes and schedules.
Modern waste treatment also heavily relies on the application of cutting-edge recycling strategies. These methods include pyrolysis, which converts natural materials into bio-oil or gas at high temperatures without the use of combustion. This technique is perfect for large-scale operations because it can handle many types of waste at once.
Additionally, these cutting-edge techniques frequently entail the use of automated sorting machinery that can distinguish between various types of materials based on their physical characteristics, such as weight or electromagnetic attraction.
Another promising strategy used in bright cities to properly manage strong wastes while producing clean energy is waste-to-energy conversion. Through a variety of processes, including combustion, gasification, anaerobic digestion, among others, non-recyclable wastes are transformed into functional heat, electricity, or fuel, thereby simultaneously reducing landfill usage and carbon emissions.
However, cutting-edge composting techniques are being used to lessen natural waste while improving soil fertility. These techniques, which range from vermicomposting (using earthworms ) tobokashi ( a Japanese fermentation technique ), each have unique advantages for effectively managing organic wastes in a smart city ecosystem while promoting environmental sustainability.
How can bright air quality monitoring and waste management be incorporated into a smart city system that is effective?
It is possible to develop a system that is easily interconnected and where careful trash handling coincides with vigilant monitoring of atmospheric cleanliness by utilizing the power of cutting-edge technologies. An intelligent infrastructure that combines bright waste management and air quality monitoring systems can help with this.
This integration is necessary for sustainable development because effective waste treatment lowers pollution and enhances air quality. A system like this could use Internet of Things ( IoT ) applications to gather real-time data from a variety of sensors placed strategically throughout the city.
The next stage entails meticulous data analysis of the information gathered. The advanced analytics platform would find patterns, trends, and anomalies in the levels of waste production and air pollution, giving decision-making processes important information. By enabling cross-platform communication between various systems within the smart city framework, technology integration is crucial in this situation.
Forecast algorithms could also be used to forecast potential increases in pollution levels or future waste generation rates.
By promoting awareness of responsible consumption habits and their effects on air quality, this integrated approach not merely improves urban environmental health but also encourages responsible living among citizens.
Such a framework also makes it easier for government agencies and relevant organizations to create efficient waste management strategies while upholding ideal air quality standards.
Therefore, combining bright waste management with air quality monitoring is a crucial component of an effective smart city system that ensures minimal ecological impact while promoting healthier cities.